One of most common yet very very important topic of Macroeconomics which is also considered to be one of the fundamental economic issue that is “INFLATION”. A general definition of Inflation is
Inflation is a rise in the general Price Level
Remember, Inflation is not an increase in ALL prices rather an increase in general level of prices and costs.
Inflation Formula
We calculate inflation by taking or measuring the rate of change of Price index of one year to another.
Price Index are weighted averages of the prices of individual products
This formula depicts that the rate of inflation is basically a percentage change in the PRICE LEVEL. But the major issue is the construction of Price Indexes.
Three Parts of Inflation
-
Low Inflation
-
Galloping Inflation
-
Hyperinflation
Low Inflation
-
Prices Rises Slowly
-
Prices are Predictable
-
Single Digit Inflation
-
In such cases, Investors trust money
-
Also, people are willing to lend money.
Galloping Inflation
-
Double digit and Tripe Digit inflation
-
Very High Inflation
-
Countries with Weak and Poor Governments
-
War or countries with conflict
-
Countries going through Revolutions or Political Turmoil
-
Iran, Brazil, Argentina, China etc
-
In such Inflation, rapid money value loss.
-
Money holding/transaction lessen
-
So at low interest rates, people don’t lend money.
Hyperinflation
-
Prices rise to million or trillion percent per year.
-
Creates a disastrous situation in economies.
-
Such an example can be of Afghanistan after the Russian war where people took money in baskets and got products in hands.
-
Real value of currency totally collapses and the transaction between debtors and creditors distorts.
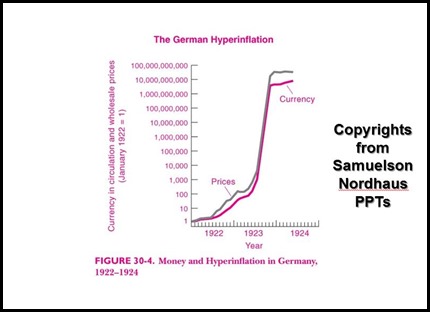
An Example of Germany Hyper Inflation with reference to the Book of Samuelson and Nordhaus
(Up next: Impact of Inflation over an Economy)



I’ve been playing on pg66bet lately, and I’m actually enjoying it. Good variety of slots and the payouts have been decent. Give pg66bet a try!
Been trying my luck with Milan Night Matka Satta. It’s a gamble, sure, but the adrenaline rush is real! Give milannightmatkasatta a shot, why not?
Thinking of trying 37winbet. Is it mobile-friendly? That’s a big thing for me. Let me know your thoughts about 37winbet.
I think that is among the most significant info for me. And i am glad studying your article. However should statement on some basic things, The website style is perfect, the articles is in reality nice : D. Good process, cheers
My brother suggested I may like this web site. He was once entirely right. This put up actually made my day. You cann’t believe just how much time I had spent for this information! Thank you!
I am constantly browsing online for ideas that can benefit me. Thank you!